Let’s discuss 4 key reasons why capital expenditure is important to all organizations and the key benefits. Let’s explore the two primary types of capital expenditures – Maintenance CapEx and Growth CapEx. Examples of OpEx include costs like utilities, laptops, and employee salaries, and rent. Whereas examples of CapEx include property, plants, manufacturing equipment, and furniture.
Challenges with Capital Expenditures
It is not guaranteed that a company will achieve the expected results from its capital expenditures. Based on this result, the company may choose to either increase or decrease the amount they spend on capital expenditures. Depreciation and amortization are done because the value of most capital expenditures decreases over time, mostly through wear and tear. For instance, patents and licenses are intangible assets and thus not included in the PP&E category. They are usually physical, fixed, and non-consumable assets such as property, equipment, or infrastructure.
Use Good Budgeting Software
The net book value represents the remaining value of the asset after accounting for the accumulated depreciation. It indicates the approximate current worth of the asset in the company’s books. In some cases, the historical cost may not be readily available on the balance sheet. In such situations, you may need to consult additional sources such as company financial statements, audited reports, or management discussions and disclosures. It depends on the company’s strategy, financial position, and industry dynamics, among other factors. Investors should analyze a company’s CAPEX in the context of its overall financial performance and future growth prospects to determine whether it is a positive or negative indicator.
Examples of CapEx
Organizations invest in new technology or software to improve their processes, increase productivity, or stay competitive in their industry. Since CapEx and expenses can seem fairly similar, it can often be confusing when you actually capitalize or expense them. The decision ultimately comes down to how long you expect to receive a benefit from your expenditure. 11 Financial may only transact business in those states in which it is registered, or qualifies for an exemption or exclusion from registration requirements.
Capital Expenditures: Definition, Calculation, Uses
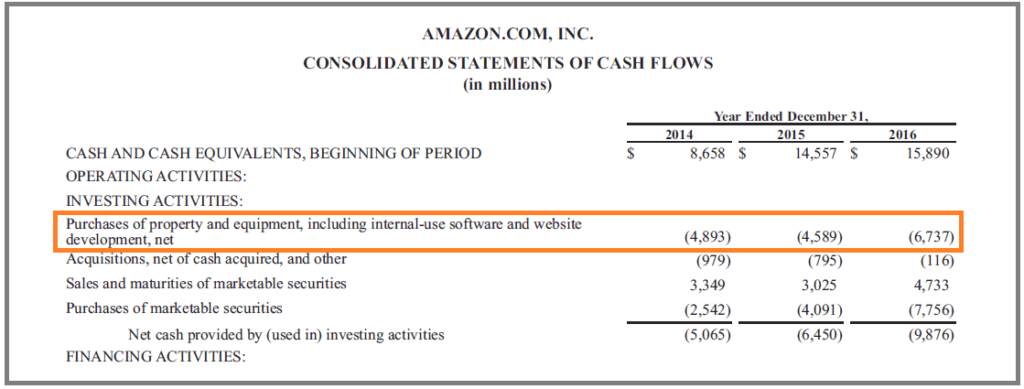
Operating expenses are shorter-term expenses that are required to meet the ongoing operational costs of running a business. Operating expenses can be fully deducted from the company’s taxes in the same year in which the expenses occur, unlike capital expenditures. CapEx can be found in the cash flow from investing activities in a company’s cash flow statement. You may see it listed as capital spending, purchases of property, plant, and equipment (PP&E), or acquisition expenses.
- However, the increased pace of production and packing can lead to higher productivity and ultimately more sales and profits.
- This is especially important for organizations that are looking to grow and stay competitive in their industry.
- The decision ultimately comes down to how long you expect to receive a benefit from your expenditure.
- Organizations making large investments in capital assets hope to generate predictable outcomes.
- CapEx, or capital expenditure, is a financial term that refers to the funds allocated by the company for the purchase of long-term assets.
It is important to differentiate capital expenditures from regular repairs and maintenance expenses that are considered operating expenses. Accurately determining the historical cost of long-term assets is crucial for calculating capital expenditures. It forms the basis for understanding the initial investment made by the company and provides a starting point for evaluating the financial performance and return on investment of these assets. By establishing the historical cost, you can proceed to the next step and account for accumulated depreciation. When calculating capital expenditures, it is important to focus on expenditures that increase the value or usefulness of the asset, extend its useful life, or improve its productivity or efficiency.
The current period depreciation expense appears as a line item on the income statement. The reduction in the cash balance of an entity is reflected in the balance sheet at the end of the taxable year. In addition, it is mentioned in the investing activities section that includes the purchase of property, plant, and equipment. CapEx is simply the money a company pours into the buying, upgrading, and maintaining of long-term assets. These investment decisions are critical to an organization due to hefty initial costs, irreversibility, and long-term effects. Similarly, telecommunication, manufacturing, and utility industries also require substantial investments.
The company was able to enhance its competitive position, meet evolving market demands, and achieve sustainable growth. In the CapEx formula, the change in PPE reflects the net investment made in tangible assets during the accounting period. By subtracting the beginning PPE from the ending PPE, you can determine the net change in asset value. Adding back the depreciation expense accounts for the reduction in asset value due to wear and tear, ensuring that CapEx reflects the actual investment in new or improved assets.
It does not include expenses paid to maintain existing assets at their current condition or return assets to their previous condition, if broken or damaged. If the expense can be considered a repair or routine maintenance, how to calculate capex from balance sheet it cannot be CapEx. CapEx impacts the balance sheet by increasing the value of long-term assets, the income statement through depreciation, and the cash flow statement as a cash outflow under investing activities[1].
It represents the cash outflows that are intended to generate future benefits and enhance the company’s productive capacity. CapEx valuation refers to the process of assessing and determining the value of capital expenditures made by an organization. It involves evaluating the expected return on investment (ROI) and the financial impact of the capital project. In conclusion, Capital Expenditures are a fundamental aspect of financial management.
Capital expenditures are different from operating expenses, which are incurred in the day-to-day functioning of a business. On the other hand, growth capital expenditure focuses on investments aimed at expanding a company’s operations, increasing production capacity, or entering new markets. It involves the acquisition of new assets, such as machinery, technology, or real estate, to support business growth. Before investing in capital expenditures, you should make sure to thoroughly analyze the expected ROI and the potential sustainability it offers. This analysis can be challenging, but with effective cash flow management software, you can streamline the process.